12 luglio 2022
Here is the first image of the JAMES WEBB space telescope!
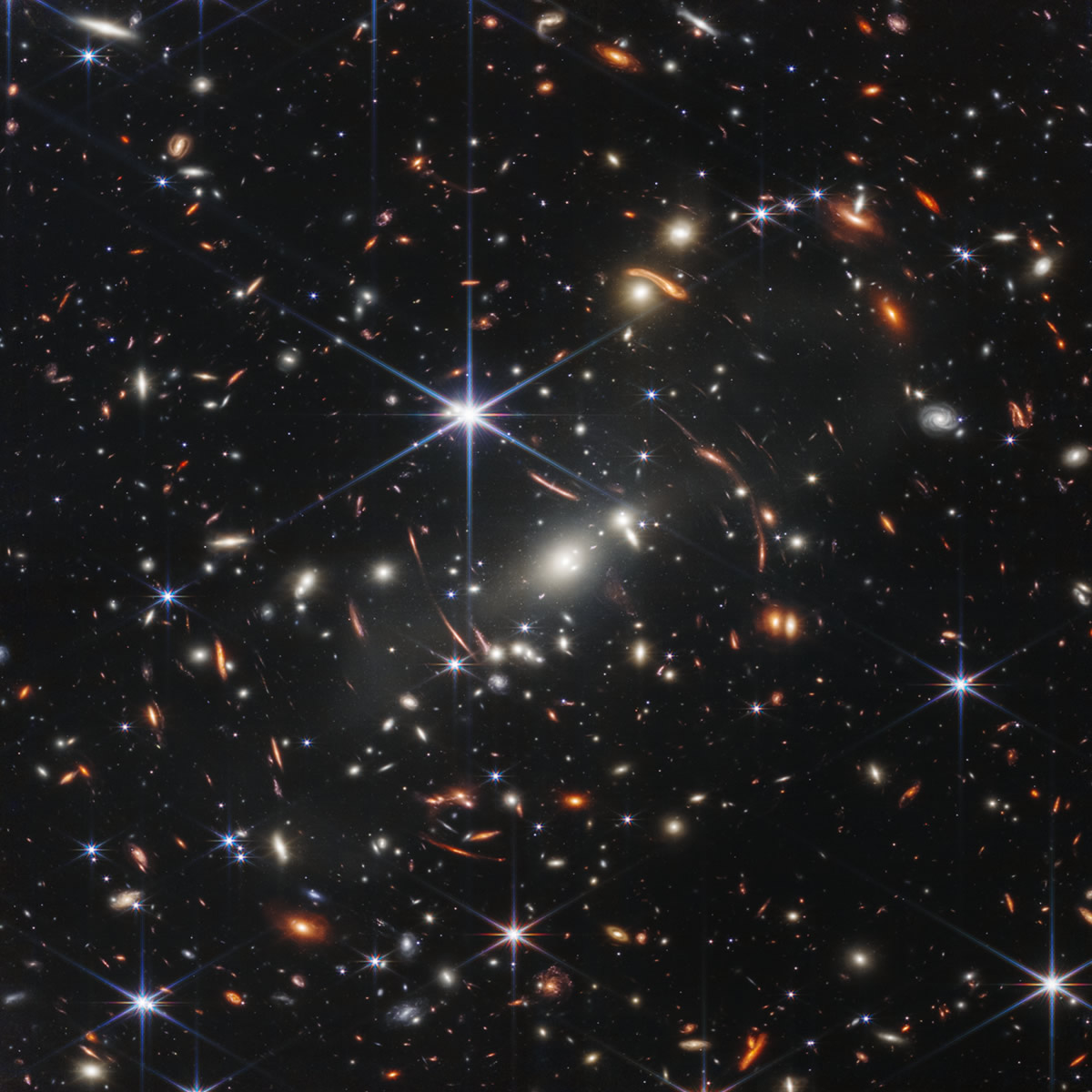
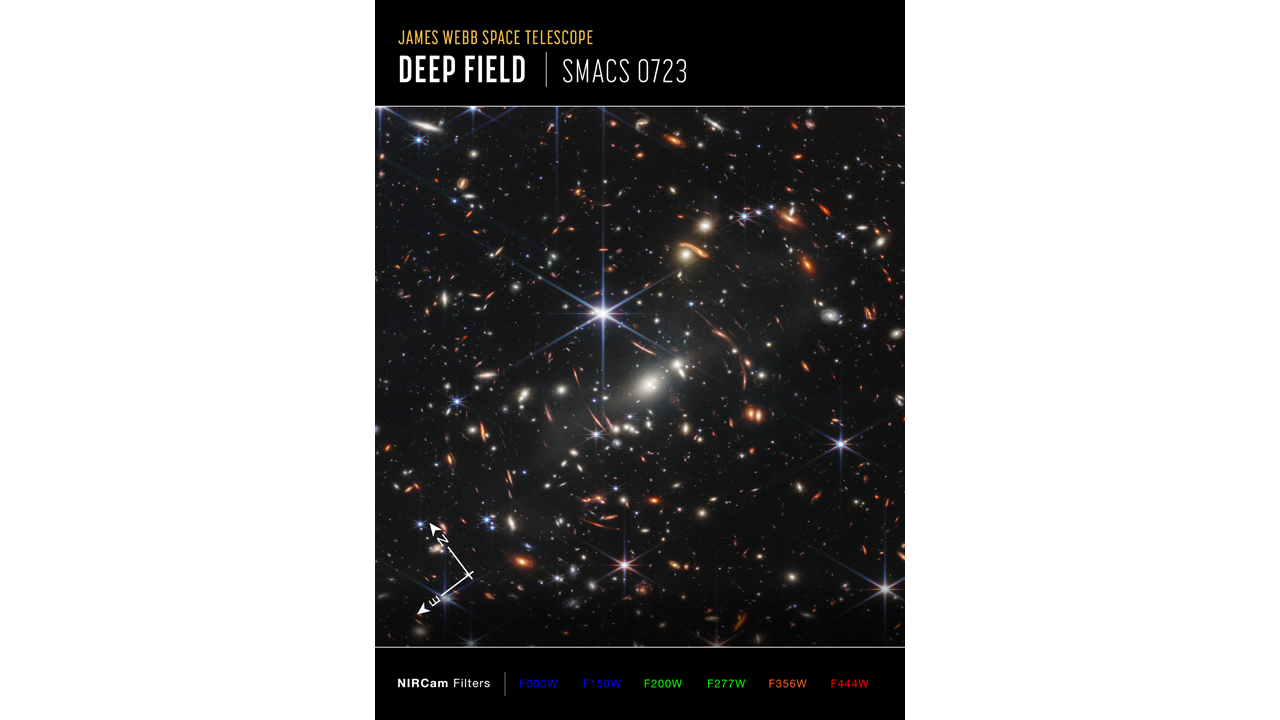
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has produced the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe to date. Known as Webb's first deep field, this image of the SMACS 0723 galaxy cluster is bursting with detail. Thousands of galaxies, including the faintest objects ever observed in infrared, appeared for the first time at Webb's sight. This slice of the vast universe is about the size of a grain of sand held at arm's length from someone on the ground looking up at the sky. This deep field, captured by Webb's NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), is a composition of images at different wavelengths, for a total of 12.5 hours of exposure, reaching depths at infrared wavelengths well beyond fields deeper than the Hubble Space Telescope, which took weeks to accomplish. The image shows the SMACS 0723 galaxy cluster as it appeared 4.6 billion years ago. The combined mass of this cluster of galaxies acts as a gravitational lens, magnifying galaxies far behind it (those slightly curved red-orange lines surrounding the center of the photograph). Webb's NIRCam has focused on those distant galaxies - they have tiny, faint structures that have never been seen before, including star clusters and diffuse features. Researchers will soon begin to learn more about the masses, ages, histories and compositions of galaxies, as Webb goes in search of the first galaxies in the universe. This image is among the telescope's first color images. The full suite will be released on Tuesday, July 12, starting at 10:30 am EDT, during a NASA live TV. Further information can be found at this link
03 March 2021
Images, videos and sounds from Perseverance, Mars
The Perseverance rover continues to amaze us. Every day NASA sends images, videos and even the first sounds from the planet Mars. The Mars 2020 Perseverance rover will investigate a region of Mars where the ancient environment may have been conducive to microbial life, probing Martian rocks for evidence of past life. During his investigation, he will collect soil and rock samples and place them at strategic points on the surface for potential return to Earth on a future mission. A spectacular video of the landing phase on the red planet is available on youtube at this link or under the side images. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory website is constantly updated and shows all the images, videos and even the sounds of Mars. To listen to the sounds go to this link - SOUNDS FROM MARS


The Perseverance landing sequence
01 December 2020
Farewell to Arecibo radio-telescope
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has decided today that a gradual closure of the Arecibo observatory, for years the largest radio telescope in the world with its 305m in diameter, will be initiated on the island of Puerto Rico.
A painful but inevitable decision: the National Science Foundation, which manages the facility, has been adamant. The radio telescope is too damaged and there is no way to safely repair it. It will be dismantled.
This is only the conclusion of a long saga of doom. The Arecibo radio telescope was built 57 years ago, and with its 305 meters in diameter it was the largest in the world for over 50 years. In 2017, the structure suffered heavy damage from Hurricane Maria, one of the most destructive to hit the island of Puerto Rico. This summer, in August, an auxiliary cable snapped, falling on the telescope's disc and damaging it further.
The structure was subjected to inspections to determine its condition and repairability, but in October another cable, this time a main one and also considered relatively healthy, broke, ruining the disc and damaging it even more.
The result of the inspections came today, with the decision by the National Science Foundation to decommission the facility. Almost all cables show wear and corrosion too advanced, some of the towers supporting the central platform could collapse without warning on the surrounding structures. And once a crumbling structure begins to collapse there is no way to stop the process. Breaking another cable would increase the load on the remaining cables, already damaged by age, even more, and this could cause a domino effect with the uncontrolled destruction of the entire telescope.
And therefore Arecibo will be dismantled, in the most controlled way possible and "accompanying" what is the now inevitable complete collapse of the structure.
Arecibo is famous for his role in the film Contact, and in the SETI project commissioned by Carl Sagan.
The demolition of Arecibo will leave a great void in all radio astronomy enthusiasts and in scientific research in general.
UPDATE 1/12/2020
As foreseen by the NSF engineers, the main telescope structure collapsed due to the breakage of additional support cables. You can see the video on the right


22 september 2020
The greatest digital camera in the world is astronomical
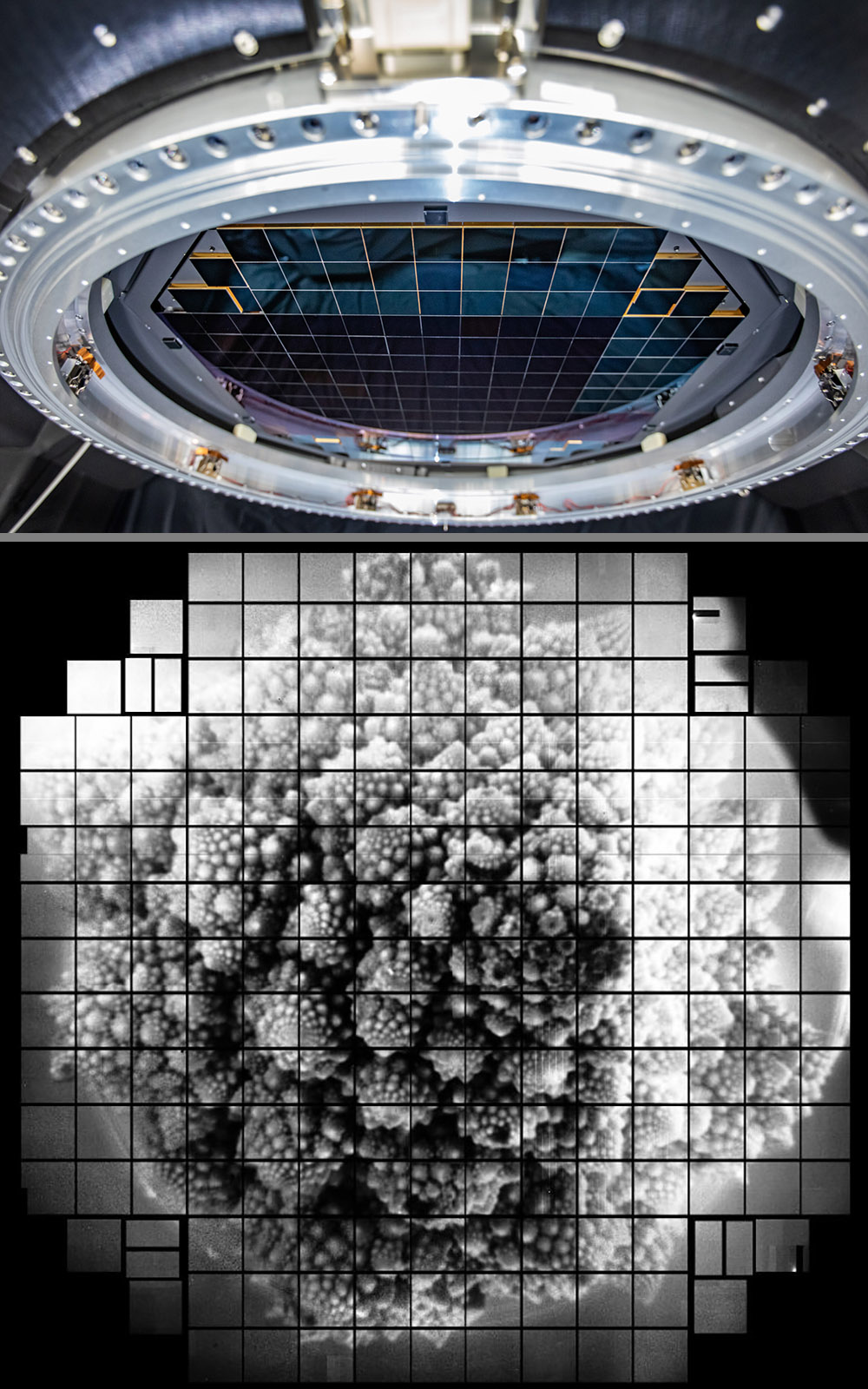
Scientists from the Slac (Stanford Linear Accelerator Center) National Accelerator Laboratory - one of the 17 national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy - have finally tested the camera of the future Vera C. Rubiin Observatory, The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST): the incredible resolution reached is 3200 Megapixel. The 3.2 billion pixels are made with an extraordinary array of 189 individual sensors, or charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each with a resolution of 16 megapixels, about the same as the imaging sensors of most modern digital cameras. One such test was to take the first 3200 megapixel images of a variety of objects, including a Romanesco broccoli, chosen for its highly detailed surface texture. The resulting images are so large that 378 ultra-high-definition 4K TV screens would be required to display just one full-size, and their resolution is so high that you could see a golf ball from about 15 miles away.
16 August 2020
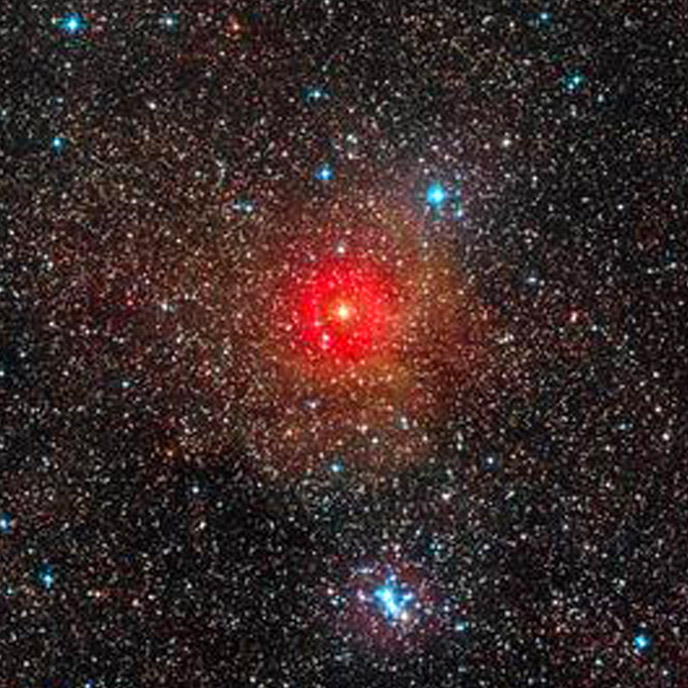
Perhaps the Betelgeuse mystery is solved, the star would be obscured by an eruption
A gigantic eruption would be the most probable cause of the sudden decrease in brightness of the star Betelgeuse, which at the turn of 2019 and 2020 had caused astronomers to worry enough to suspect an imminent explosion. Its mystery was solved by the Hubble Space Telescope, owned by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA): thanks to its ultraviolet observations, it was possible to identify the expulsion from the stellar surface of an enormous quantity of incandescent material, which it would then form a cloud of dust responsible for the clouding. The study results are published in The Astrophysical Journal. Here the direct link to the article
According to the researchers 'reconstruction, from September to November 2019 a huge mass of ultra-hot plasma rose from the surface of Betelgeuse to head towards its external atmosphere: from there it continued to travel for millions of kilometers, cooling and turning into a' immense cloud of dust, the very one that for months obscured about a quarter of the surface of the red supergiant, making it almost unrecognizable until April.
"With Hubble we observed the material as it left the visible surface of the star and receded through its atmosphere, before the dust formed that obscured it," explains Andrea Dupree, associate director of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. in Cambridge. "We could thus see the effect of a dense, hot region moving outward from the southeastern portion of the star. It was material two to four times brighter than the star's normal brightness. Then, about a month later, the southern hemisphere of Betelgeuse darkened noticeably as the star became paler. We think it is possible that the emission detected by Hubble produced a dark cloud "

30 July 2020
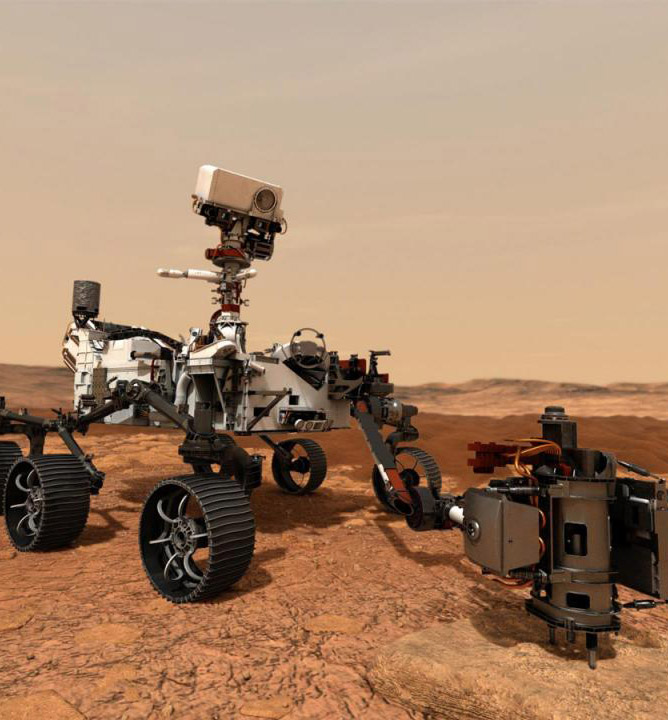
Perseverance, the NASA mission left for Mars
NASA's Mars 2020 mission launched, the third direct to Mars that started in the last ten days after those of the United Arab Emirates and China. The launch took place from the US Air Force base in Cape Canaveral with an Atlas 5 rocket and leads to Mars Perseverance, the fifth NASA rover to land on the red planet, this time to lead the way for future missions with astronauts and to search for traces of past life or perhaps present.
The most sophisticated robot ever sent to another planet will touch the ground of Mars on February 18, 2021 in the Jezero crater, the ancient river bed in which sediments, where there was water billions of years ago, will look for fossil traces of life past and ice beneath the surface, starting to test the technologies that will one day allow, even human crews, this new, great leap.

3 July 2020
A 10 years images time-lapse of the Sun (NASA)
A single video for ten years of the Sun's life condensed into a time-lapse of just over an hour. The spectacular video, which you can watch on the side, is the result of the assembly work of scientists at the Goddard Space Flight Center of NASA, with thousands of photos collected over 10 years by the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), the space telescope launched in 2010 to study our star.
The Solar Dynamics Observatory has captured over 425 million images, totaling 20 million gigabytes of data, showing phenomena otherwise invisible to our eyes. The mounted shots, one for each hour of observation from 2 June 2010 to 1 June 2020, also show details and features related to the solar corona, the outermost part of the Sun's atmosphere, with its constantly moving plasma particles.
Among the most beautiful moments, the one that happened between 5 and 6 June 2012 (12:24 minutes). You can see a round and dark spot that crosses the frame: it is the planet Venus, whose next transit in front of the solar disk will take place only in 2117.